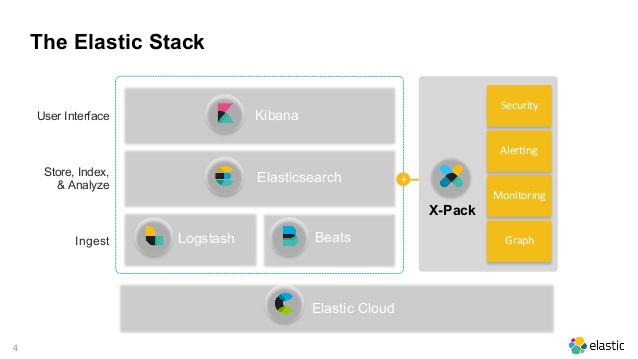
What's Elasticsearch
Wikipedia:
Elasticsearch is a search engine based on the Lucene library. It provides a distributed, multitenant-capable full-text search engine with an HTTP web interface and schema-free JSON documents. Elasticsearch is developed in Java and is released as open source under the terms of the Apache License. Official clients are available in Java, .NET (C#), PHP, Python, Apache Groovy, Ruby and many other languages.5 According to the DB-Engines ranking, Elasticsearch is the most popular enterprise search engine followed by Apache Solr, also based on Lucene.
Executing SELECT * FROM … all the time consumes a lot of CPU also it doesn’t have index, One solution would be using FTS (Full Text Search) in RDBMS but in NoSQL world If you need a high performance search engine you’d better use Elasticsearch.
History
- 1999 - Lucene
- It helped all search engines back then index the data that they were adjusting from the internet and provide reasonable ways of retrieving that information based fuzzy matching.
- 2004 - Compass
- Built on top of Lucene, the same services but in a more scalable manner, idea was to provide a distributed search solution.
- 2010 - Elasticsearch
- Distributed, RESTful search and analytical engine
Use cases
- Security/log analytics
- Marketing = Use this data to find things:
- How people find our website?
- Where they came from?
- What device they are using?
- What part of the world they are coming from?
- Search = ES was built with idea of great search engine
Concepts
- Near Real Time (NRT)
- Cluster:
- collection of our nodes
- has a unique name
- Node:
- part of the cluster to store the data
- has a unique name
- Index:
- a collection of similar documents
- Type:
- a category or a partition of your index
- Document:
- in JSON format
- customer
- event
Querying
- Simple query:
- get all accounts: GET bank/account/_search
- get all accounts in state of CA:
- multiple conditions:GET bank/account/_search { "query": { "match": { "state": "CA" } } }GET bank/account/_search { "query": { "bool": { "state": "CA" } } }- boost: 3 = three times more important than state
_score: How ES identifies the relevance of a document based on your search query
Bulk loading data into Elasticsearch
_bulk: The endpoint for bulk api, this is where we send request to when we want to bulk load data. it expects new-line delimited JSON data (including a new-line at the very end, which is important, otherwise we’ll get errors). It allows us to Index, Create, Delete, Update. When using this we need to make sure we are using --data-binary flag from the curl command.
- /_bulk
- new-line JSON
- Index, Create, Delete, Update
- —data-binary
How to bulk load data
- Create a file that has some data in it:
{ "index" : { "_index" : "indexName", "_type" : "typeName", "_id": "1" }}
{"title":"Web Developer II","author":"Chrysler Clerk","content":"Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Proin risus. Praesent lectus.","publishedDate":"2018-02-03T17:51:14Z"}
- Load the data into Elasticsearch using curl:
curl -s -H "Content-Type: application/x-ndjson" -XPOST localhost:9200/_bulk --data-binary "@reqs"; echo